Embark on a mathematical journey with Dividing Polynomials Quiz Part 1, a comprehensive exploration of the art of polynomial division. From the fundamental concepts to advanced techniques, this quiz will challenge your understanding and equip you with the skills to conquer any polynomial division problem.
As you delve into this quiz, you’ll uncover the secrets of polynomial division algorithms, synthetic division, long division, and more. With each question, you’ll strengthen your grasp on the techniques and develop a deeper appreciation for the elegance of polynomial mathematics.
Introduction: Dividing Polynomials Quiz Part 1
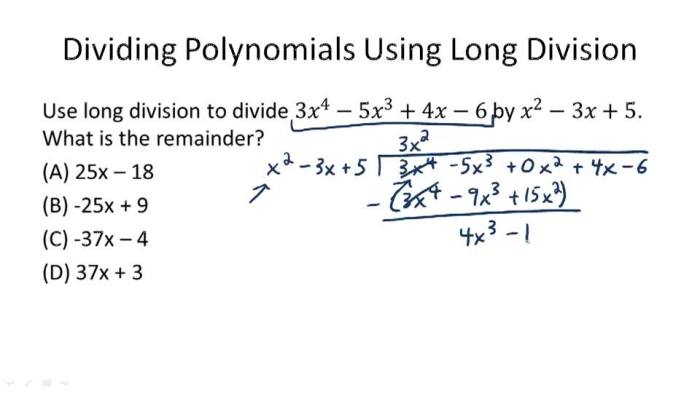
Polynomial division is a mathematical process that involves dividing one polynomial (the dividend) by another polynomial (the divisor) to obtain a quotient and a remainder. The quotient is a polynomial that represents the number of times the divisor fits into the dividend, while the remainder is the part of the dividend that cannot be divided evenly by the divisor.
The dividing polynomials quiz is designed to assess your understanding of the polynomial division process. The quiz will present you with a series of polynomial division problems, and you will be required to solve each problem by finding the quotient and the remainder.
Overview of the Dividing Polynomials Quiz
- The quiz consists of 10 polynomial division problems.
- Each problem is worth 10 points.
- You will have 60 minutes to complete the quiz.
- You may use a calculator to assist you in solving the problems.
Dividing Polynomials Algorithm
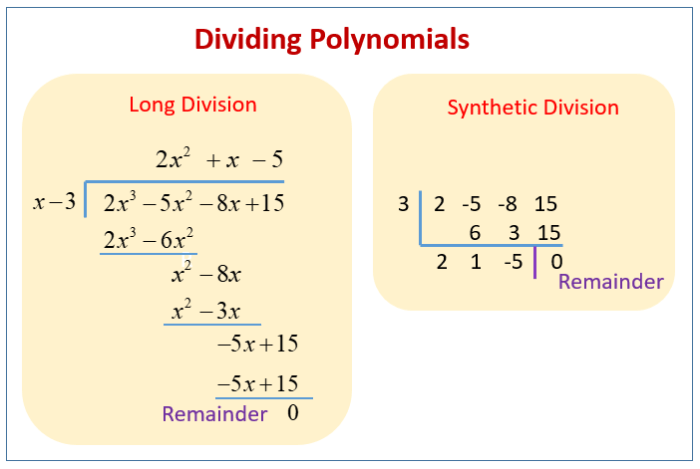
In mathematics, polynomial division is an algorithm that divides one polynomial by another, resulting in a quotient polynomial and a remainder polynomial. This process is similar to long division for integers, but with polynomials.
Steps Involved in Dividing Polynomials Algorithm
- Arrange the polynomials in descending order of their degrees.
- Divide the first term of the dividend by the first term of the divisor.
- Multiply the divisor by the result obtained in step 2.
- Subtract the result obtained in step 3 from the dividend.
- Bring down the next term of the dividend.
- Repeat steps 2 to 5 until the degree of the remainder is less than the degree of the divisor.
Example, Dividing polynomials quiz part 1
Divide the polynomial x3– 2x 2+ x – 2 by x- 1 .
x2– x + 2
x- 1 ) x3– 2x 2+ x – 2
– ( x3– x 2)
——————-
– x2+ x
– (- x2+ x )
——————-
2
Therefore, the quotient is x2– x + 2 and the remainder is 2.
Synthetic Division
Synthetic division is a method for dividing a polynomial by a linear factor of the form (x – a) without performing the long division process. This method is particularly useful when the divisor is a simple linear factor and the dividend is of a higher degree.
Step-by-Step Guide to Synthetic Division
- Write the coefficients of the dividend in a row, with the missing terms represented by 0.
- Bring down the first coefficient of the dividend.
- Multiply the coefficient by the constant a and write the result below the next coefficient.
- Add the coefficients in the next column and write the result below the line.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 for the remaining coefficients.
- The last number in the bottom row is the remainder, and the other numbers are the coefficients of the quotient.
Table Demonstrating the Process
| Coefficient | Dividend | Divisor | Quotient | Remainder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x2 | x3 + 2x2
|
x
|
x2+ 4x + 11 | 22 |
Long Division
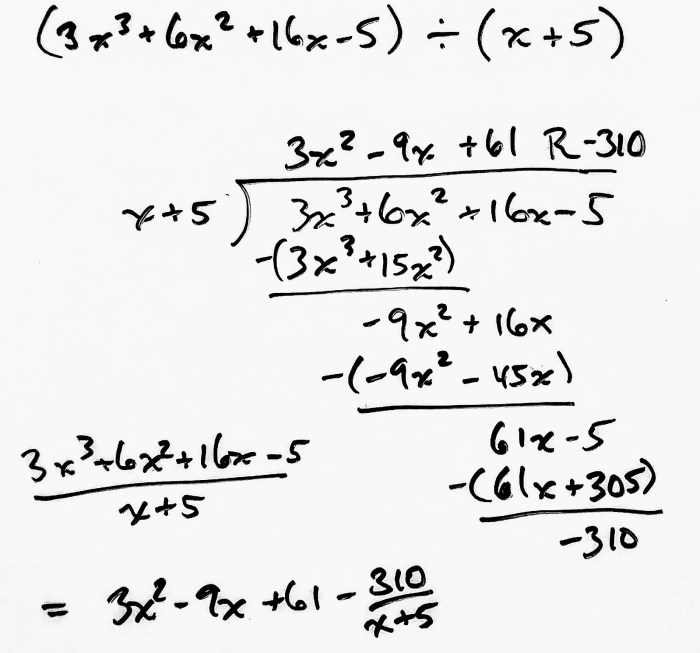
Long division is a method for dividing one polynomial by another, resulting in a quotient and a remainder. This process is useful for solving equations, finding roots, and simplifying expressions.
To perform long division of polynomials, follow these steps:
- Arrange the polynomials in descending order of degree, with the dividend (the polynomial being divided) on top and the divisor (the polynomial dividing) on the bottom.
- Divide the first term of the dividend by the first term of the divisor, and write the result above the line, directly above the second term of the dividend.
- Multiply the divisor by the result obtained in step 2, and write the product below the dividend.
- Subtract the product obtained in step 3 from the dividend.
- Bring down the next term of the dividend.
- Repeat steps 2-5 until the degree of the remainder is less than the degree of the divisor.
- The polynomial above the line is the quotient, and the polynomial below the line is the remainder.
Worked Example
Divide the polynomial x3– 2 x2+ 5 x– 6 by the polynomial x– 2.
| Dividend | Divisor | Quotient | Remainder |
|---|---|---|---|
x3
|
x
|
x2
|
0 |
In this example, the quotient is x2– 2 x+ 3, and the remainder is 0.
Remainder Theorem
The Remainder Theorem states that when a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x
a), the remainder is equal to f(a).
This theorem is useful in polynomial division as it allows us to quickly determine the remainder without having to perform the entire division process. It can also be used to find the roots of a polynomial by setting the remainder to zero and solving for a.
Example, Dividing polynomials quiz part 1
Find the remainder when the polynomial f(x) = x^3 – 2x^2 + 3x – 4 is divided by (x – 2).
Using the Remainder Theorem, we can substitute x = 2 into f(x) to get the remainder:
f(2) = (2)^3
- 2(2)^2 + 3(2)
- 4 = 8
- 8 + 6
- 4 = 2
Therefore, the remainder when f(x) is divided by (x – 2) is 2.
Factor Theorem
The Factor Theorem states that if a polynomial f(x) has a factor (x – a), then a is a root of the polynomial, meaning f(a) = 0.
This theorem is significant in polynomial division as it allows us to determine whether a given binomial (x – a) is a factor of the polynomial f(x) by evaluating f(a). If f(a) = 0, then (x – a) is a factor of f(x).
Using the Factor Theorem to Find Roots of Polynomials
The Factor Theorem can be used to find roots of polynomials by systematically evaluating the polynomial at different values of x until we find a value that makes the polynomial equal to zero. If we find a value of x that makes the polynomial equal to zero, then we have found a root of the polynomial.
Clarifying Questions
What is polynomial division?
Polynomial division is a mathematical operation that divides one polynomial (the dividend) by another polynomial (the divisor), resulting in a quotient and a remainder.
What is synthetic division?
Synthetic division is a simplified method of polynomial division that involves arranging the coefficients of the dividend and divisor in a table and performing a series of operations to obtain the quotient and remainder.
What is the Remainder Theorem?
The Remainder Theorem states that when a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x – a), the remainder is equal to f(a).
What is the Factor Theorem?
The Factor Theorem states that if (x – a) is a factor of a polynomial f(x), then f(a) is equal to zero.