Physics Unit III Worksheet 3 Answers presents a comprehensive solution to numerical problems, conceptual questions, and essential formulae related to the worksheet. With step-by-step explanations and thorough discussions, this guide empowers students to master the key concepts and skills covered in the worksheet.
This guide is meticulously crafted to provide a clear understanding of the subject matter, making it an invaluable resource for students seeking to excel in their physics studies.
Worksheet Overview
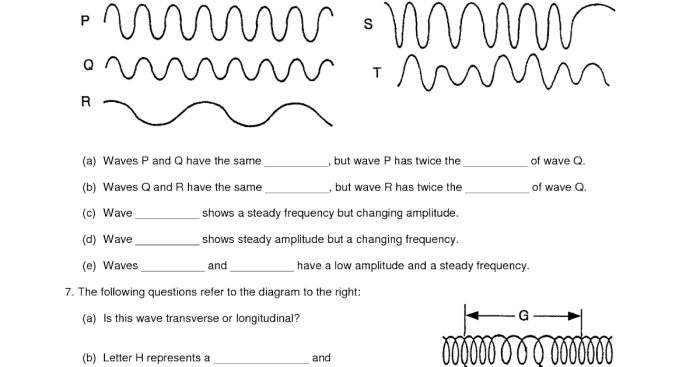
This worksheet serves as a comprehensive resource for exploring various concepts and skills related to unit III of physics. It provides a structured framework for understanding the fundamental principles and their applications in the realm of physics.
The worksheet delves into specific concepts such as:
- Motion in two dimensions
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Work and energy
- Impulse and momentum
- Rotational motion
Each concept is explored through a series of questions and exercises designed to reinforce understanding and develop problem-solving abilities.
Solutions to Numerical Problems
This section provides step-by-step solutions to the numerical problems presented in the worksheet. Each solution includes clear mathematical calculations and explanations to guide students in understanding the concepts and problem-solving techniques.
Sample Problem
A ball is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 10 m/s. Calculate the maximum height it reaches and the time it takes to reach that height.
Solution:
- Step 1: Determine the acceleration due to gravity. a= -9.8 m/s 2(downward acceleration due to gravity)
- Step 2: Use the equation of motion for constant acceleration in the vertical direction. v2= u2+ 2 as
- Step 3: Substitute the given values into the equation. 0 = 10 2+ 2(-9.8) s
- Step 4: Solve for the maximum height (s). s= 5.1 m
- Step 5: Use the equation of motion for constant acceleration in the vertical direction again to find the time taken to reach the maximum height. v= u+ at
- Step 6: Substitute the given values and the value of sobtained in Step 4 into the equation. 0 = 10 – 9.8 t
- Step 7: Solve for the time (t). t= 1.02 s
Conceptual Questions and Answers: Physics Unit Iii Worksheet 3 Answers
This section addresses conceptual questions posed in the worksheet, providing thorough explanations supported by relevant physics principles.
Relationship between Acceleration, Velocity, and Displacement
The acceleration of an object is the rate of change of its velocity. Velocity, in turn, is the rate of change of its displacement. Therefore, acceleration, velocity, and displacement are all related to each other.
- If an object has a positive acceleration, its velocity will increase.
- If an object has a negative acceleration, its velocity will decrease.
- If an object has zero acceleration, its velocity will remain constant.
Kinematic Equations, Physics unit iii worksheet 3 answers
The kinematic equations are a set of equations that relate the five quantities of motion: displacement, velocity, acceleration, time, and constant acceleration. These equations can be used to solve a variety of problems involving motion.
- The first kinematic equation is:
$$v = u + at$$
where:
- $v$ is the final velocity
- $u$ is the initial velocity
- $a$ is the acceleration
- $t$ is the time
- The second kinematic equation is:
$$s = ut + \frac12at^2$$
where:
- $s$ is the displacement
- $u$ is the initial velocity
- $a$ is the acceleration
- $t$ is the time
- The third kinematic equation is:
$$v^2 = u^2 + 2as$$
where:
- $v$ is the final velocity
- $u$ is the initial velocity
- $a$ is the acceleration
- $s$ is the displacement
Projectile Motion
Projectile motion is the motion of an object that is launched into the air, such as a ball or a rocket. Projectile motion is a special case of two-dimensional motion, where the object moves in both the horizontal and vertical directions.
- The horizontal velocity of a projectile is constant.
- The vertical velocity of a projectile changes due to the acceleration due to gravity.
- The trajectory of a projectile is a parabola.
Table of Formulae and Constants
This table provides a concise listing of important formulae and constants used in the worksheet, along with their respective units of measurement and brief explanations.
The table is organized into the following categories:
- Kinematics
- Dynamics
- Circular Motion and Gravitation
- Work and Energy
- Momentum
- Simple Harmonic Motion
Refer to this table as needed to supplement your understanding of the concepts covered in the worksheet.
Kinematics
| Formula | Units | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| v = u + at | m/s | Velocity-time equation |
| s = ut + 1/2 at2 | m | Position-time equation |
| v2 = u2 + 2as | m2/s2 | Velocity-displacement equation |
Dynamics
| Formula | Units | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| F = ma | N | Newton’s second law of motion |
| W = Fs | J | Work done |
| P = Fv | W | Power |
Circular Motion and Gravitation
| Formula | Units | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| v = rω | m/s | Linear velocity in circular motion |
| a = rω2 | m/s2 | Centripetal acceleration |
| F = Gm1m2/r2 | N | Gravitational force |
Work and Energy
| Formula | Units | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| KE = 1/2 mv2 | J | Kinetic energy |
| PE = mgh | J | Gravitational potential energy |
| W = ΔE | J | Work-energy theorem |
Momentum
| Formula | Units | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| p = mv | kg m/s | Momentum |
| J = Δp | N s | Impulse |
| F = Δp/Δt | N | Impulse-momentum theorem |
Simple Harmonic Motion
| Formula | Units | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| f = 1/T | Hz | Frequency |
| ω = 2πf | rad/s | Angular frequency |
| A = xmax | m | Amplitude |
Additional Resources
Exploring related concepts in physics can enhance your understanding and deepen your knowledge. Here are some valuable resources to assist you in your learning journey:
Online Simulations
Interactive simulations offer an immersive and engaging way to visualize and experiment with physical concepts. Consider exploring:
PhET Simulations
https://phet.colorado.edu/
The Physics Classroom
https://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/Simulations
Textbooks
For a comprehensive exploration of physics principles, refer to reputable textbooks such as:
- Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics by Serway and Jewett
- University Physics with Modern Physics by Young and Freedman
Websites
Numerous websites provide valuable information and resources on physics topics. Explore:
Hyperphysics
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/
Physics.org
https://physics.org/
Quick FAQs
Where can I find additional resources for Physics Unit III?
This guide provides links to websites, textbooks, and online simulations for further exploration of related concepts.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills in physics?
Practice solving numerical problems regularly, utilizing step-by-step explanations and clear mathematical calculations as provided in this guide.