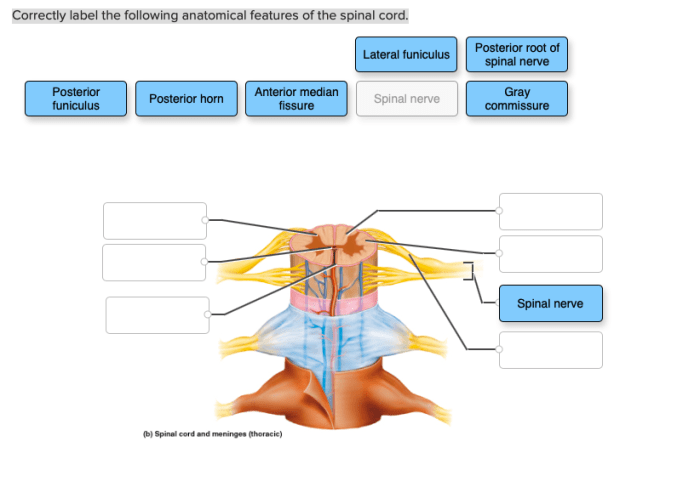
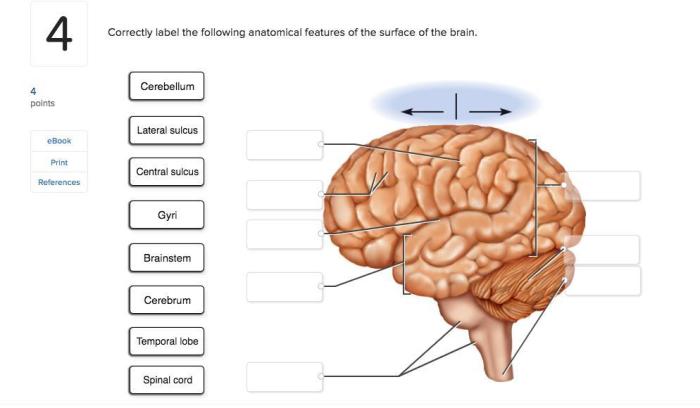
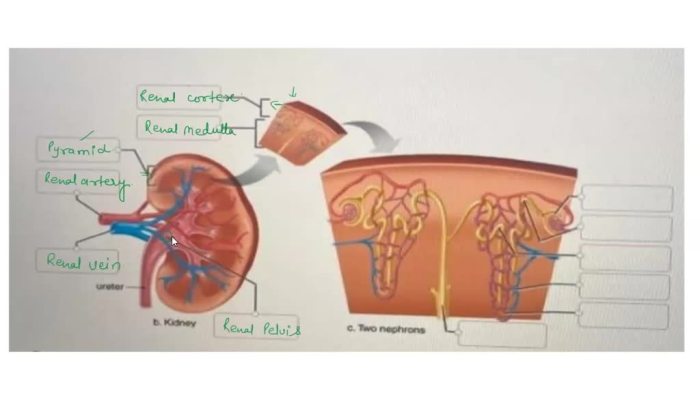
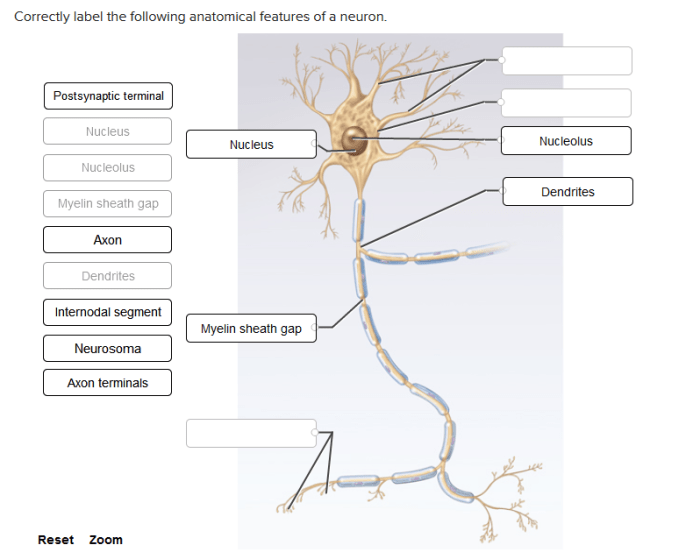
Correctly label the anatomical features of the otolithic membrane – Delving into the intricacies of the otolithic membrane, this discourse embarks on a comprehensive exploration of its structure, function, and clinical significance. As a crucial component of the vestibular system, the otolithic membrane plays a pivotal role in maintaining balance and equilibrium.
Understanding its intricate anatomical features is essential for comprehending its physiological functions and potential pathological implications.
Composed of a gelatinous matrix embedded with calcium carbonate crystals known as otoconia, the otolithic membrane is strategically positioned within the utricle and saccule of the inner ear. Its unique structure and innervation enable it to detect linear acceleration and gravity, providing essential sensory information for spatial orientation and balance control.
Otolithic Membrane Overview: Correctly Label The Anatomical Features Of The Otolithic Membrane
The otolithic membrane is a specialized sensory structure within the inner ear that plays a crucial role in the vestibular system, responsible for maintaining balance and equilibrium. It consists of two distinct regions: the utricle and the saccule.The utricle is located in the horizontal plane of the inner ear and is involved in detecting linear acceleration in the horizontal plane.
The saccule, on the other hand, is positioned in the vertical plane and is responsible for detecting linear acceleration in the vertical plane.Both the utricle and the saccule contain a gelatinous membrane known as the otolithic membrane. This membrane is covered in small, calcium carbonate crystals called otoconia.
The otoconia provide the membrane with density, allowing it to respond to changes in gravitational forces and linear acceleration.
Anatomical Features, Correctly label the anatomical features of the otolithic membrane
The otolithic membrane is a complex structure with several distinct anatomical features:
- Utricle:The utricle is a sac-like structure located in the horizontal plane of the inner ear. It contains the otolithic membrane, which is covered in otoconia.
- Saccule:The saccule is another sac-like structure located in the vertical plane of the inner ear. It also contains the otolithic membrane with otoconia.
- Maculae:The maculae are specialized sensory areas located within the utricle and saccule. They contain hair cells that are embedded in the otolithic membrane.
- Otoconia:Otoconia are small, calcium carbonate crystals that cover the otolithic membrane. They provide the membrane with density and allow it to respond to changes in gravitational forces and linear acceleration.
The table below summarizes the anatomical features of the otolithic membrane and their functions:| Feature | Function ||—|—|| Utricle | Detects linear acceleration in the horizontal plane || Saccule | Detects linear acceleration in the vertical plane || Maculae | Sensory areas containing hair cells || Otoconia | Provide density and allow response to gravitational forces and linear acceleration |
Answers to Common Questions
What is the function of the otolithic membrane?
The otolithic membrane is responsible for detecting linear acceleration and gravity, providing essential sensory information for balance and spatial orientation.
What are the key anatomical features of the otolithic membrane?
The key anatomical features of the otolithic membrane include the utricle, saccule, maculae, and otoconia.
How is the otolithic membrane innervated?
The otolithic membrane is innervated by the vestibular nerve, which transmits sensory information to the brain.