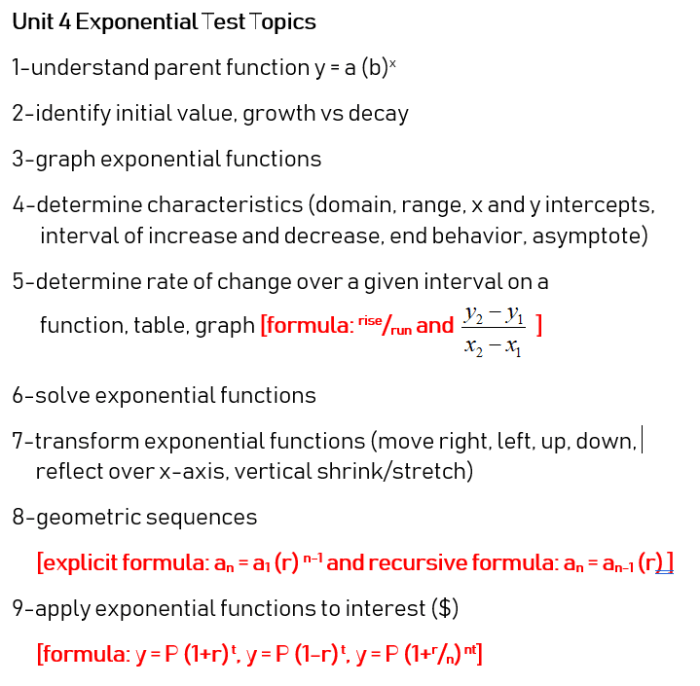
The unit 4 exponential functions answer key provides a comprehensive guide to exponential functions, encompassing their definition, properties, graphing techniques, transformations, solving methods, and real-world applications. This key serves as an invaluable resource for students seeking to master the intricacies of exponential functions.
Exponential functions are mathematical functions that exhibit exponential growth or decay, characterized by a constant base raised to a variable exponent. They possess unique properties, including asymptotic behavior, monotonicity, and continuity, which are essential for understanding their behavior.
Exponential Functions Overview
Exponential functions are a class of mathematical functions that describe the rate of growth or decay of a quantity over time. They are characterized by their distinctive shape, which is a curve that either increases or decreases exponentially.
Exponential growth occurs when the rate of growth is proportional to the size of the population, leading to a rapid increase over time. Conversely, exponential decay occurs when the rate of decrease is proportional to the size of the population, resulting in a gradual decline.
Exponential functions have numerous applications in real-world scenarios, including finance, science, and technology. For instance, compound interest in banking follows an exponential growth pattern, while radioactive decay in physics follows an exponential decay pattern.
Properties of Exponential Functions
Asymptotic Behavior
Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote, which is a horizontal line that the function approaches as the input value tends to infinity. The asymptote represents the limiting value that the function will never reach.
Monotonicity
Exponential functions are either increasing or decreasing depending on the base of the exponential expression. Functions with a base greater than 1 are increasing, while those with a base less than 1 are decreasing.
Continuity
Exponential functions are continuous for all real numbers, meaning there are no breaks or jumps in the graph.
Graphing Exponential Functions
To graph an exponential function, follow these steps:
- Find the y-intercept by evaluating the function at x = 0.
- Determine the base of the exponential expression. If the base is greater than 1, the function is increasing, and if the base is less than 1, the function is decreasing.
- Plot the y-intercept and draw the horizontal asymptote.
- Create a table of values to plot additional points.
- Connect the points with a smooth curve.
Different types of exponential graphs include:
- Increasing exponential graphs (base > 1)
- Decreasing exponential graphs (base< 1)
- Exponential growth graphs (y-intercept > 0)
- Exponential decay graphs (y-intercept > 0)
Transformations of Exponential Functions
Exponential functions can be transformed by applying various transformations, including:
Vertical Shifts, Unit 4 exponential functions answer key
Vertical shifts move the graph up or down. Adding a constant to the function moves the graph up, while subtracting a constant moves the graph down.
Horizontal Shifts
Horizontal shifts move the graph left or right. Adding a constant to the input value moves the graph left, while subtracting a constant moves the graph right.
Reflections
Reflections flip the graph across the x-axis or y-axis. Multiplying the function by -1 reflects the graph across the x-axis, while multiplying the input value by -1 reflects the graph across the y-axis.
Solving Exponential Equations: Unit 4 Exponential Functions Answer Key
Exponential equations can be solved using various methods, including:
Logarithmic Functions
Taking the logarithm of both sides of an exponential equation transforms it into a linear equation that can be solved for the unknown variable.
Factoring
If the exponential expression can be factored, the equation can be solved by setting each factor equal to zero and solving for the variable.
Graphing
Graphing the exponential function and the horizontal line y = 0 allows for the determination of the solution(s) by finding the points of intersection.
Applications of Exponential Functions
Exponential functions have numerous applications in various fields, including:
Finance (Compound Interest)
Compound interest is calculated using an exponential function, where the initial investment grows exponentially over time due to the addition of interest.
Science (Population Growth)
Population growth can be modeled using an exponential function, assuming a constant growth rate.
Technology (Radioactive Decay)
Radioactive decay follows an exponential decay pattern, where the amount of radioactive substance decreases exponentially over time.
FAQ
What are the key properties of exponential functions?
Exponential functions exhibit asymptotic behavior, monotonicity, and continuity.
How do you solve exponential equations?
Exponential equations can be solved using logarithmic functions, factoring, or graphing.
What are some real-world applications of exponential functions?
Exponential functions are used in finance (compound interest), science (population growth), and technology (radioactive decay).