Choose the affirmative usted command – The affirmative usted command, a cornerstone of Spanish grammar, plays a crucial role in conveying politeness and formality. This guide delves into the intricacies of the affirmative usted, providing a comprehensive overview of its conjugation, usage, and significance.
The affirmative usted is employed in formal and respectful situations, addressing individuals with respect and distance. Its usage extends beyond addressing strangers to encompass interactions with acquaintances, superiors, and elders, reflecting the cultural norms of Spanish-speaking societies.
Define the Affirmative Usted

The affirmative usted is a formal Spanish form of address used to show respect or distance. It is the third-person singular form of the verb and is used when speaking to someone who is not familiar or who is in a position of authority.
The affirmative usted is used in all tenses and moods of the Spanish verb. It is conjugated according to the following rules:
Conjugation of the Affirmative Usted
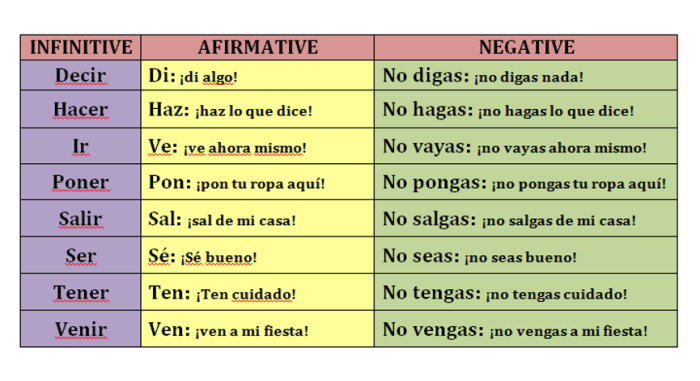
Regular Verbs, Choose the affirmative usted command
- Present tense: -ar verbs: -a; -er and -ir verbs: -e
- Preterite tense: -ar verbs: -ó; -er and -ir verbs: -ió
- Imperfect tense: -ar verbs: -aba; -er and -ir verbs: -ía
- Future tense: -ar verbs: -ará; -er and -ir verbs: -erá
- Conditional tense: -ar verbs: -aría; -er and -ir verbs: -ería
Irregular Verbs
| Verb | Present | Preterite | Imperfect | Future | Conditional |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ser | es | fue | era | será | sería |
| estar | está | estuvo | estaba | estará | estaría |
| haber | hay | hubo | había | habrá | habría |
| ir | va | fue | iba | irá | iría |
| ver | ve | vio | veía | verá | vería |
Usage of the Affirmative Usted

The affirmative usted is used in a variety of situations, including:
- When speaking to someone who is older or in a position of authority
- When speaking to someone who is not familiar
- When writing formal letters or emails
- When making public announcements
The affirmative usted is not used when speaking to friends or family members. It is also not used when speaking to children.
Comparison with Other Spanish Forms
Affirmative Tú
The affirmative tú is the informal form of address used when speaking to someone who is familiar. It is conjugated according to the following rules:
- Present tense: -ar verbs: -as; -er and -ir verbs: -es
- Preterite tense: -ar verbs: -aste; -er and -ir verbs: -iste
- Imperfect tense: -ar verbs: -abas; -er and -ir verbs: -ías
- Future tense: -ar verbs: -arás; -er and -ir verbs: -erás
- Conditional tense: -ar verbs: -arías; -er and -ir verbs: -erías
Negative Usted
The negative usted is used to express negation in the formal form of address. It is conjugated according to the following rules:
- Present tense: -ar verbs: -a; -er and -ir verbs: -e
- Preterite tense: -ar verbs: -ó; -er and -ir verbs: -ió
- Imperfect tense: -ar verbs: -aba; -er and -ir verbs: -ía
- Future tense: -ar verbs: -ará; -er and -ir verbs: -erá
- Conditional tense: -ar verbs: -aría; -er and -ir verbs: -ería
Examples of the Affirmative Usted

- ¿Cómo está usted?
- ¿Qué tal está usted?
- Le agradezco su ayuda.
- Le felicito por su éxito.
- Le deseo un feliz cumpleaños.
Expert Answers: Choose The Affirmative Usted Command
What is the purpose of the affirmative usted command?
The affirmative usted command is used to convey politeness and formality in Spanish, expressing respect and distance in various social interactions.
When should the affirmative usted command be used?
The affirmative usted command should be used in formal settings, when addressing strangers, acquaintances, superiors, and elders, as well as in written communication such as letters and emails.
How is the affirmative usted command conjugated?
The affirmative usted command is conjugated by adding the appropriate ending to the verb stem. For regular verbs, the endings are -ar, -er, and -ir. For irregular verbs, the endings vary depending on the verb.
