Internal venturing is a more attractive strategy than acquisitions when organizations seek to foster innovation, leverage existing resources, and mitigate integration risks. This engaging analysis delves into the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches, providing insights into when each strategy is most appropriate.
Internal venturing involves developing new businesses or products within an existing organization, while acquisitions entail purchasing external entities to gain access to new markets or capabilities. Understanding the key characteristics of each strategy is crucial for making informed decisions.
Internal Venturing vs. Acquisitions: Overview
Internal venturing is a strategic approach within an organization that fosters innovation and entrepreneurship by creating new ventures or businesses internally. It involves developing and commercializing new products, services, or technologies within the existing organizational structure. In contrast, acquisitions refer to the purchase of an existing company or business entity to gain access to its assets, capabilities, or market share.
Internal venturing and acquisitions are distinct strategies with unique characteristics and implications for organizations.
Key Characteristics of Internal Venturing
- Involves creating new ventures within the organization.
- Leverages existing resources and capabilities.
- Focuses on fostering innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Requires significant investment and commitment.
Key Characteristics of Acquisitions, Internal venturing is a more attractive strategy than acquisitions when
- Involves purchasing an existing company or business entity.
- Provides access to new markets, technologies, or capabilities.
- Can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Requires careful integration and management.
Advantages of Internal Venturing
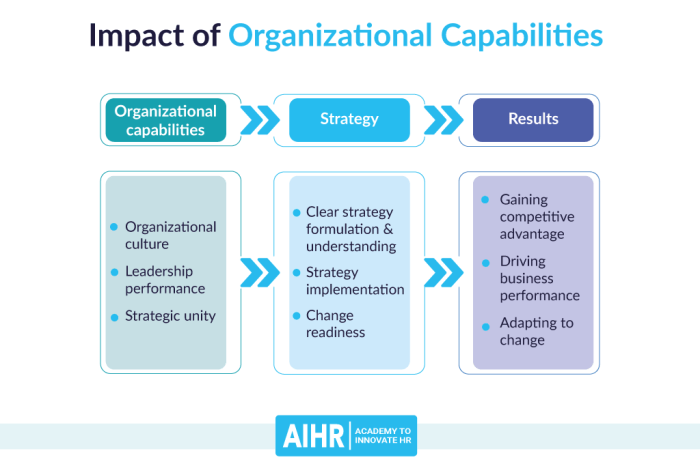
Internal venturing offers several potential benefits for organizations:
- Fosters Innovation and Entrepreneurship:Internal venturing creates an environment that encourages employees to generate and pursue new ideas, leading to increased innovation and entrepreneurial spirit within the organization.
- Leverages Existing Resources and Capabilities:By utilizing existing resources and capabilities, internal venturing can minimize the need for external investments and reduce the risk associated with developing new ventures.
- Protects Intellectual Property:Internal ventures developed within the organization maintain intellectual property rights, ensuring that the organization retains control over its innovations.
- Cultural Alignment:Internal ventures are aligned with the organization’s culture and values, fostering a sense of ownership and commitment among employees.
Disadvantages of Internal Venturing
Internal venturing also has potential drawbacks that organizations should consider:
- Limited Scope:Internal ventures may be constrained by the organization’s existing capabilities and resources, limiting the scope and potential impact of new ventures.
- Bureaucratic Hurdles:Large organizations may have bureaucratic processes that can hinder the agility and decision-making required for successful internal ventures.
- Lack of External Perspective:Internal ventures may lack the fresh perspectives and expertise that external acquisitions can provide.
- Resource Competition:Internal ventures may compete with existing business units for resources, leading to potential conflicts and resource allocation challenges.
Advantages of Acquisitions
Acquisitions offer organizations several potential advantages:
- Access to New Markets, Technologies, and Capabilities:Acquisitions provide a quick and effective way to gain access to new markets, technologies, or capabilities that may be difficult or costly to develop internally.
- Leverage External Expertise and Resources:Acquiring companies with specialized expertise or resources can bring valuable knowledge and capabilities to the organization.
- Increased Market Share:Acquiring competitors or complementary businesses can increase the organization’s market share and competitive advantage.
- Synergies:Acquisitions can create synergies by combining the strengths and resources of two organizations, leading to increased efficiency and profitability.
Disadvantages of Acquisitions
Acquisitions also have potential drawbacks that organizations should consider:
- Cost and Time:Acquisitions can be expensive and time-consuming, requiring significant financial resources and management attention.
- Integration Challenges:Integrating acquired companies into the organization can be challenging, leading to disruption, cultural clashes, and employee resistance.
- Loss of Control:Acquisitions involve surrendering some degree of control to the acquired company, which may impact decision-making and strategic direction.
- Cultural Misalignment:Acquiring companies with different cultures or values may create challenges in aligning and motivating employees.
FAQ Compilation: Internal Venturing Is A More Attractive Strategy Than Acquisitions When
What is the primary advantage of internal venturing?
Internal venturing fosters innovation and entrepreneurship within organizations by leveraging existing resources and capabilities.
When is acquisition a more suitable strategy?
Acquisitions are advantageous when organizations seek rapid access to new markets, technologies, or expertise that cannot be developed internally.
What are the key factors to consider when choosing between internal venturing and acquisitions?
Factors to consider include industry dynamics, company size, risk tolerance, and the availability of internal resources and capabilities.