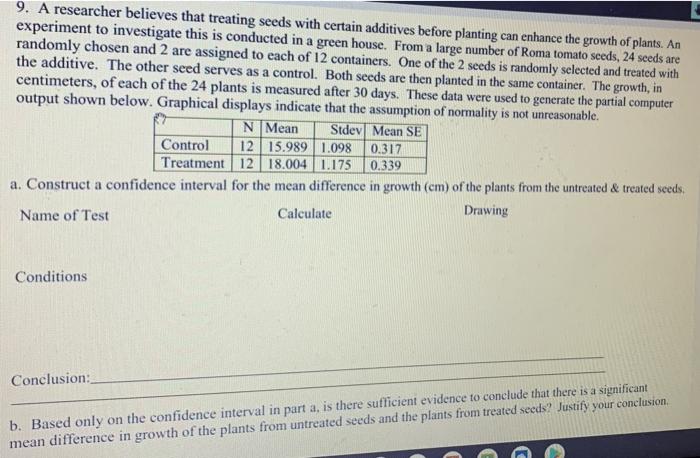
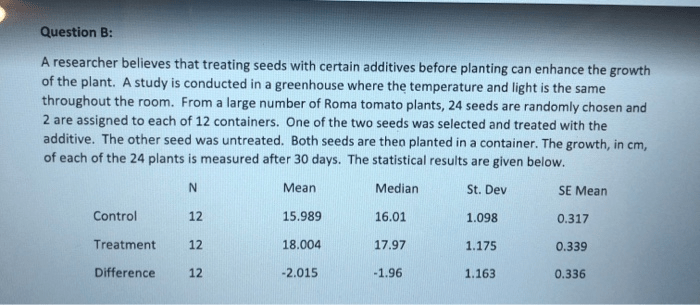
As a researcher believes that treating seeds with certain additives takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The utilization of additives in seed treatment has emerged as a transformative practice, offering a myriad of benefits that can significantly enhance crop productivity and sustainability. This comprehensive exploration delves into the types of additives commonly employed, their specific functions, and the mechanisms by which they promote seed performance.
Furthermore, it examines the various seed treatment methods, comparing their advantages and disadvantages to guide informed decision-making.
Seed Treatment Additives: A Researcher Believes That Treating Seeds With Certain Additives

Seed treatment additives enhance seed performance and promote plant growth. These additives include:
- Fungicides: Protect seeds from fungal diseases.
- Insecticides: Control insect pests that damage seeds.
- Bactericides: Prevent bacterial infections.
- Nutrients: Provide essential nutrients for seedling growth.
- Plant growth regulators: Stimulate seed germination and seedling development.
- Hydrogels: Improve seed hydration and protect against drought stress.
Seed Treatment Methods
Seed treatment methods include:
- Pelleting: Coating seeds with a layer of additives.
- Film coating: Applying a thin film of additives to seeds.
- In-furrow application: Adding additives directly to the soil during planting.
- Soaking: Submerging seeds in a solution of additives.
Impact on Seed Germination and Growth, A researcher believes that treating seeds with certain additives
Additives improve seed germination and growth by:
- Protecting seeds from pathogens and pests.
- Providing essential nutrients for seedling development.
- Stimulating seed germination and seedling growth.
- Improving seed hydration and protecting against drought stress.
Environmental Implications
Additives can have environmental impacts, such as:
- Soil contamination: Additives can accumulate in soil, potentially affecting soil health.
- Water pollution: Additives can leach into water sources, potentially harming aquatic life.
Economic Considerations
Additives can be cost-effective, providing a return on investment by:
- Increasing crop yields.
- Reducing seed losses due to pests and diseases.
- Improving seedling vigor and establishment.
Regulatory Aspects
Additives are regulated to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Future Directions
Future research will focus on:
- Developing novel additives and delivery systems.
- Integrating precision agriculture techniques into seed treatment practices.
- Minimizing environmental impacts of additives.
Helpful Answers
What are the most commonly used additives in seed treatment?
Commonly used additives in seed treatment include fungicides, insecticides, growth regulators, and micronutrients.
How do additives enhance seed performance?
Additives can improve seed germination, seedling growth, and crop yield by protecting against pathogens, stimulating physiological processes, and providing essential nutrients.
What are the potential environmental implications of using additives in seed treatment?
While additives can enhance crop production, their use must be carefully managed to minimize potential environmental impacts, such as soil and water contamination.