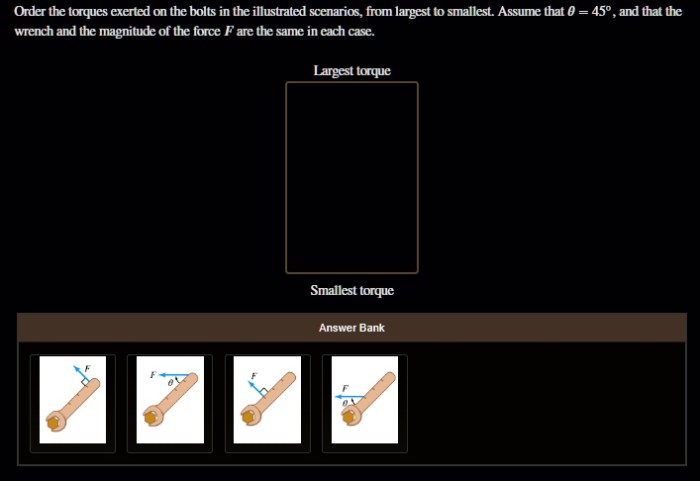
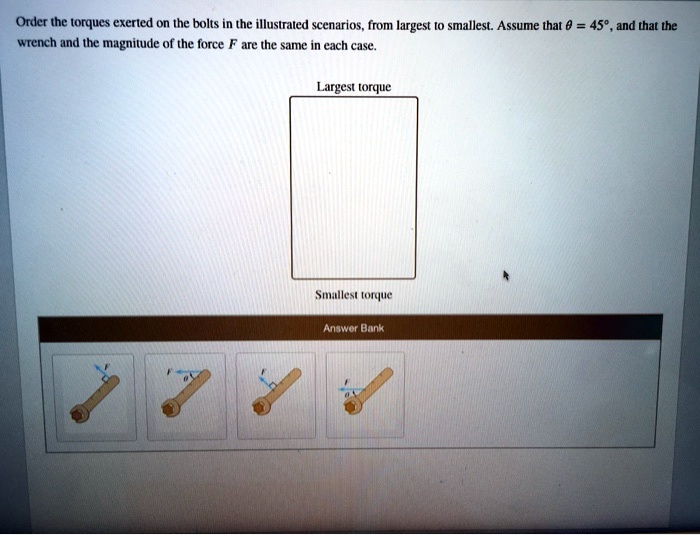
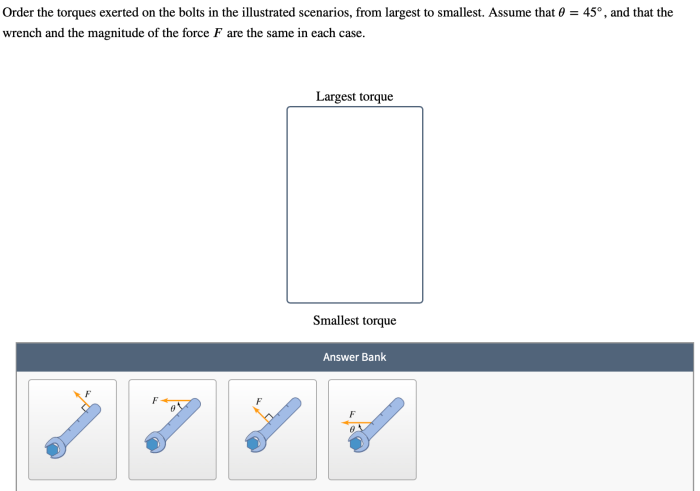
Order the torques exerted on the bolts is a critical aspect of ensuring the integrity and performance of bolted joints. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of torque sequencing, explores the factors influencing torque exertion, and provides best practices for ordering torques in various applications.
By understanding the principles and techniques Artikeld in this guide, engineers and technicians can effectively order torques on bolts, ensuring the safety and reliability of bolted connections.
Bolt Torque Order: Order The Torques Exerted On The Bolts
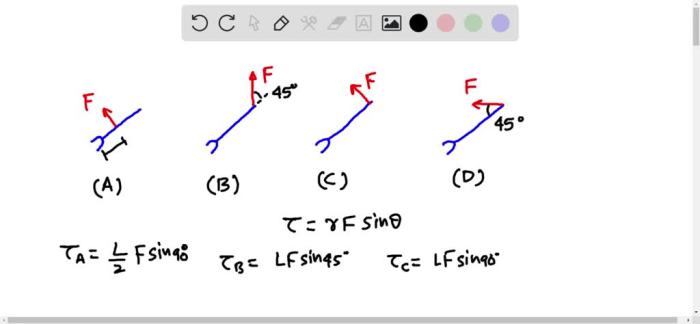
Proper torque sequencing is essential for ensuring the integrity and performance of bolted joints. It involves tightening bolts in a specific order and pattern to evenly distribute the load and prevent damage to the bolts or the surrounding components.
Incorrect torque sequencing can lead to several issues, including:
- Uneven load distribution, leading to premature bolt failure.
- Over-tightening of some bolts, causing thread damage or bolt breakage.
- Under-tightening of other bolts, resulting in loose connections and potential joint failure.
For different bolt configurations, specific torque sequencing patterns should be followed. For example:
- Four-bolt pattern:Tighten the bolts in a star pattern, starting from the center and moving outwards.
- Six-bolt pattern:Tighten the bolts in a hexagonal pattern, starting from any corner and alternating sides.
- Eight-bolt pattern:Tighten the bolts in a circular pattern, starting from any bolt and moving around the circumference.
Factors Influencing Torque Exertion
The torque exerted on bolts is influenced by several key factors:
- Bolt size:Larger bolts require higher torque to achieve the same level of tightness.
- Bolt material:Different materials have different yield strengths, which affects the amount of torque required to tighten the bolt.
- Lubrication:Lubricating the bolt threads reduces friction, allowing for easier tightening and more accurate torque measurement.
- External forces:Vibration and temperature can affect the torque required to maintain a tight connection.
Measurement and Verification
Accurate torque measurement is crucial for ensuring proper bolt performance. Common methods used include:
- Torque wrenches:Manual or electronic devices that measure the torque applied to the bolt.
- Torque indicators:Visual indicators that change color or deformation when a specific torque is reached.
Proper calibration and maintenance of these devices is essential to ensure accurate torque readings.
Torque Charts and Specifications
Manufacturers provide torque specifications for various bolt sizes and materials. Adhering to these specifications is essential for:
- Preventing over-tightening, which can damage bolts or components.
- Ensuring proper clamping force, which is critical for maintaining joint integrity.
- Meeting safety and performance requirements.
Special Considerations
Specific applications may require special considerations for torque ordering:
- Structural bolts:High-strength bolts used in critical structural applications require precise torque sequencing to ensure load-bearing capacity.
- Automotive bolts:Torque specifications for automotive bolts vary depending on the component and application.
- Industrial machinery bolts:Proper torque sequencing is essential for maintaining proper alignment and preventing vibration-induced loosening.
Best Practices, Order the torques exerted on the bolts
Best practices for ordering torques on bolts include:
- Proper bolt selection based on load requirements and material compatibility.
- Use of appropriate torque tools and calibration.
- Inspection and maintenance of bolted joints to ensure proper torque retention.
FAQs
What is the significance of torque sequencing?
Torque sequencing ensures that bolts are tightened in a specific order and to a specific torque value, preventing uneven loading and potential joint failure.
What factors influence the torque exerted on bolts?
Factors such as bolt size, material, lubrication, external forces, and joint design influence the torque required to achieve the desired clamping force.
How is torque measured on bolts?
Torque is typically measured using torque wrenches or other calibrated measuring devices that provide accurate readings.
Why is it important to adhere to manufacturer’s torque specifications?
Adhering to torque specifications ensures proper bolt performance, prevents over-tightening or under-tightening, and maintains the integrity of the bolted joint.