Subjunctive in noun clauses spanish – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of Spanish grammar as we delve into the intricacies of the subjunctive mood in noun clauses. This grammatical phenomenon, characterized by its unique set of rules and nuances, plays a pivotal role in conveying a myriad of ideas and emotions in Spanish discourse.
Delving into the depths of noun clauses, we will uncover their essential function within Spanish grammar. We will explore the various types of subjunctive noun clauses, each governed by its distinct set of grammatical principles. Moreover, we will unravel the common triggers that necessitate the use of the subjunctive mood in these clauses, shedding light on the rationale behind these linguistic conventions.
Introduction to Subjunctive Mood in Spanish Noun Clauses
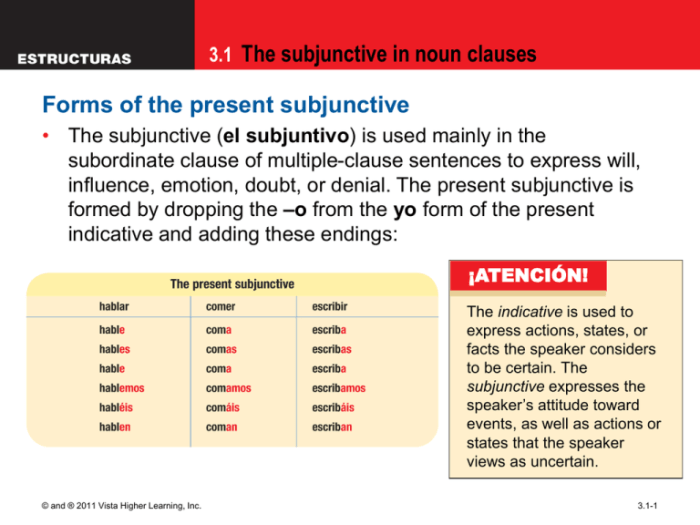
The subjunctive mood in Spanish is a grammatical form used to express uncertainty, subjectivity, or hypothetical situations. It is often used in noun clauses, which are subordinate clauses that function as nouns within a sentence.
Noun clauses can play various roles in a sentence, such as the subject, direct object, or indirect object. When a noun clause is used in a sentence, the verb within the clause must be in the subjunctive mood if the main clause contains a trigger that requires it.
Types of Subjunctive Noun Clauses
There are several types of subjunctive noun clauses, each with its own grammatical rules:
- Subject clauses: These clauses function as the subject of the main clause. They are introduced by the conjunction “que” and require the subjunctive mood if the main clause expresses emotion, doubt, or uncertainty.
- Direct object clauses: These clauses function as the direct object of the main clause. They are introduced by the conjunction “que” and require the subjunctive mood if the main clause contains a verb of influence or desire.
- Indirect object clauses: These clauses function as the indirect object of the main clause. They are introduced by the preposition “a” or “para” and require the subjunctive mood if the main clause contains a verb of telling, asking, or advising.
Triggers for Subjunctive Mood in Noun Clauses
The use of the subjunctive mood in noun clauses is triggered by specific words or phrases in the main clause. These triggers include:
- Verbs of emotion(e.g., alegrarse, enojarse, sorprenderse)
- Verbs of doubt or uncertainty(e.g., dudar, no creer, negar)
- Verbs of influence or desire(e.g., pedir, rogar, ordenar)
- Verbs of telling, asking, or advising(e.g., decir, preguntar, aconsejar)
- Expressions of possibility or probability(e.g., es posible, es probable)
Examples of Subjunctive Noun Clauses in Context, Subjunctive in noun clauses spanish
Here are some examples of subjunctive noun clauses in Spanish:
| Noun Clause | Translation | Type of Clause |
|---|---|---|
| Me alegra que hayas venido. | I’m glad you came. | Subject clause |
| Quiero que me ayudes. | I want you to help me. | Direct object clause |
| Te recomiendo que estudies más. | I recommend that you study more. | Indirect object clause |
Comparison with Indicative Mood in Noun Clauses
The subjunctive mood differs from the indicative mood in noun clauses in the following ways:
- The subjunctive moodexpresses uncertainty, subjectivity, or hypothetical situations, while the indicative mood expresses facts or certainties.
- The subjunctive moodis used when the main clause contains a trigger that requires it, while the indicative mood is used when there is no such trigger.
Exercises and Practice
To practice using the subjunctive mood in noun clauses, complete the following exercises:
- Translate the following sentences into Spanish, using the subjunctive mood where necessary:
- I hope that you will come.
- I’m not sure if she will be there.
- I asked him to help me.
FAQ Explained: Subjunctive In Noun Clauses Spanish
What is the subjunctive mood?
The subjunctive mood is a grammatical mood used to express a variety of ideas and emotions, such as uncertainty, doubt, desire, and emotion.
When is the subjunctive mood used in noun clauses?
The subjunctive mood is used in noun clauses when the main verb of the sentence expresses an emotion, opinion, or doubt.
What are the different types of subjunctive noun clauses?
There are four main types of subjunctive noun clauses: noun clauses that express desire, noun clauses that express emotion, noun clauses that express opinion, and noun clauses that express doubt.


