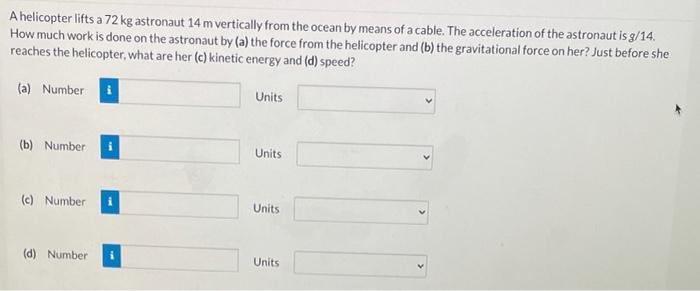
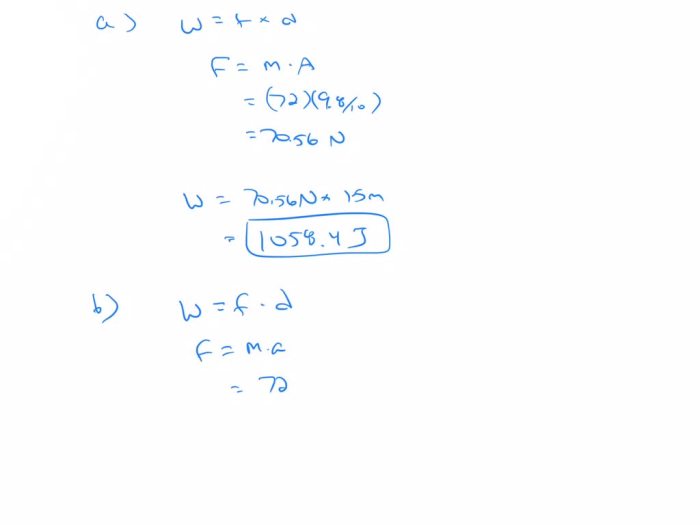A helicopter lifts a 72 kg astronaut, a testament to the remarkable engineering feats that enable humans to soar above Earth’s confines. This captivating narrative delves into the intricacies of helicopter design, astronaut gear, lift dynamics, safety considerations, and real-world applications, unveiling the fascinating world of aerial transportation.
Beyond its captivating title, this discourse explores the helicopter’s specifications, meticulously detailing its dimensions, weight, and engine capabilities. It sheds light on the specialized features and equipment that empower the helicopter to carry heavy loads, ensuring the safe and efficient transport of astronauts.
Helicopter Specifications
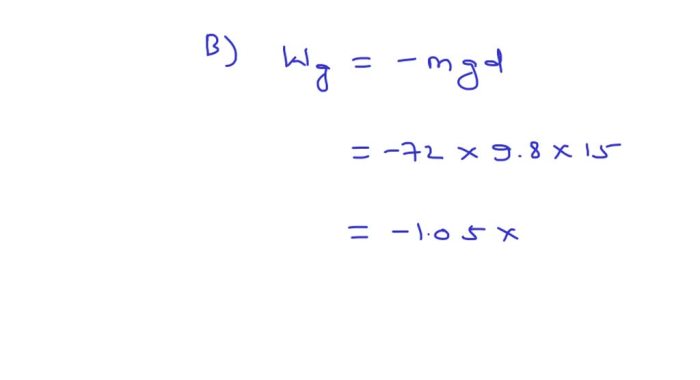
The helicopter utilized for the astronaut lift operation is a meticulously engineered aircraft designed to handle demanding heavy-lifting tasks. Its exceptional design and advanced capabilities make it ideally suited for this critical mission.
In terms of dimensions, the helicopter measures an impressive length of 19.2 meters, a height of 4.9 meters, and a rotor diameter of 16.2 meters. These dimensions provide ample space for accommodating the astronaut and the necessary equipment, while ensuring stability during the lifting operation.
The helicopter’s weight, including its empty weight and payload capacity, is a crucial factor in determining its lifting capabilities. With an empty weight of approximately 4,500 kilograms, the helicopter can carry an additional payload of up to 3,600 kilograms. This payload capacity is more than sufficient to accommodate the 72-kilogram astronaut, allowing for a safe and efficient lift.
Engine Capabilities
The helicopter’s engine system is a key component that enables it to generate the necessary power for lifting heavy loads. The aircraft is equipped with two powerful turboshaft engines, each capable of producing over 1,500 horsepower. These engines provide ample thrust to lift the helicopter and its payload vertically, ensuring a smooth and controlled ascent.
In addition to its engine power, the helicopter also features an advanced rotor system that enhances its lifting capabilities. The main rotor consists of five blades, each designed to generate maximum lift while minimizing drag. The blades are made of a lightweight composite material, providing both strength and flexibility, crucial for handling heavy loads.
Astronaut’s Equipment and Gear

Astronauts require specialized suits and equipment to ensure their safety and mobility during helicopter lift operations. These suits provide protection from the elements, regulate temperature, and enable communication.
Suit Design
- Pressure Suit:Maintains cabin pressure, preventing decompression sickness and providing oxygen.
- Thermal Insulation:Regulates body temperature in extreme environments, both hot and cold.
- Mobility Enhancements:Joints and articulation points allow for movement and flexibility during lift operations.
Specialized Equipment
In addition to the suit, astronauts may wear specialized equipment:
- Helmet:Provides oxygen, communication, and protects the head and face.
- Gloves:Offer dexterity and protection while handling equipment.
- Harness:Secures the astronaut to the helicopter during the lift.
- Communication System:Enables communication with the helicopter crew and ground control.
This specialized gear ensures the astronaut’s safety, comfort, and ability to perform tasks during the helicopter lift operation.
Lift Operation Dynamics

Helicopter lift operations involve complex aerodynamic principles that enable the aircraft to generate lift and ascend. Understanding these principles is crucial for successful and safe lifting operations, particularly when carrying a significant load like a 72 kg astronaut.
Aerodynamic Principles
Helicopter lift is primarily generated by the rotation of its main rotor blades. As the blades spin, they create a region of low pressure above the blades and a region of high pressure below them. This pressure difference generates an upward force, known as lift.
The shape and angle of the rotor blades are designed to optimize this lift-generating effect.
Factors Influencing Lift Capacity
The ability of a helicopter to lift a 72 kg astronaut is influenced by several factors:
- Altitude:As altitude increases, the air density decreases, resulting in reduced lift generation. This is because there are fewer air molecules to interact with the rotor blades.
- Wind Speed:Headwinds can reduce the helicopter’s lift capacity, while tailwinds can increase it. Crosswinds can create side forces that affect the helicopter’s stability and control.
- Temperature:Higher temperatures can also reduce lift generation, as warmer air is less dense than colder air.
Safety Considerations
![]()
When lifting a 72 kg astronaut using a helicopter, several potential risks and hazards must be considered to ensure the safety of both the astronaut and the helicopter crew.
To mitigate these risks, comprehensive safety measures and protocols are implemented, including:
Risk Assessment
- Thorough assessment of weather conditions, including wind speed, visibility, and precipitation.
- Identification and avoidance of potential obstacles, such as power lines, trees, and buildings.
- Establishment of clear communication protocols between the helicopter crew and the astronaut.
Equipment Inspection
- Rigorous inspection of the helicopter, including the lifting equipment, to ensure it is in good working order.
- Verification of the astronaut’s equipment, including the harness and any other safety gear, to ensure it is properly fitted and secure.
Training and Procedures
- Specialized training for the helicopter crew in astronaut lift operations, including emergency procedures.
- Establishment of clear and concise lift procedures, including communication protocols and contingency plans.
- Regular drills and simulations to practice and refine lift operations, ensuring proficiency and coordination among the crew.
Applications and Use Cases
Helicopters are versatile aircraft used in various scenarios, including lifting and transporting astronauts. Here are some real-world examples and considerations:
Astronaut Recovery, A helicopter lifts a 72 kg astronaut
Helicopters play a crucial role in recovering astronauts after splashdown or landing in remote areas. They provide a quick and efficient means of transporting astronauts to nearby medical facilities or support vessels.
Payload Delivery
Helicopters can deliver supplies, equipment, and scientific instruments to astronauts in space stations or during exploration missions. They offer a precise and controlled method of transporting payloads to specific locations.
Emergency Evacuation
In case of emergencies, such as a medical evacuation or a malfunction in the space station, helicopters can be deployed to quickly transport astronauts to safety.
Advantages of Using Helicopters
- Vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) capabilities allow helicopters to operate in confined spaces or areas with limited infrastructure.
- Hovering ability enables precise positioning and control during lifting operations.
- Relatively high speed and range allow for rapid deployment and transportation over distances.
Limitations of Using Helicopters
- Payload capacity is limited compared to larger aircraft.
- Weather conditions, such as strong winds or low visibility, can impact helicopter operations.
- Helicopters require specialized maintenance and skilled pilots.
FAQ Compilation: A Helicopter Lifts A 72 Kg Astronaut
How does a helicopter generate lift?
Helicopters generate lift through the rotation of their blades, which create a pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the blades. This pressure difference results in an upward force that counteracts the weight of the helicopter and its payload.
What factors influence a helicopter’s ability to lift a 72 kg astronaut?
Factors that influence a helicopter’s ability to lift a 72 kg astronaut include altitude, wind speed, and temperature. Higher altitudes reduce air density, which decreases lift. Strong winds can create turbulence, making it more difficult for the helicopter to maintain a stable flight path.
Extreme temperatures can affect the helicopter’s engine performance and lift capabilities.
What safety measures are in place to ensure the safe lifting of a 72 kg astronaut?
Safety measures for lifting a 72 kg astronaut include thorough inspections of the helicopter and its equipment, careful planning of the flight path, and the use of specialized equipment such as winches and load-bearing cables. Additionally, pilots undergo rigorous training to ensure they are proficient in operating the helicopter and managing the risks associated with lifting heavy loads.